What can a Fingerprint reveal about Sexe?

reveal about Your Sexe?
Fingerprints have been listed for a long time in a lengthy list of constitutional differences between males and females. These sexe differences typically manifest in three aspects of the fingerprints: 1) 'pattern type', 2) 'ridge breadth', and 3) 'minutiae'.
In time studies around the world revealed that usually two typical sexe differences can be observed regarding the occurence of the 4 major fingerprint pattern types. First of all: arches are typically more common in females; and secondly: whorls are more common in males.
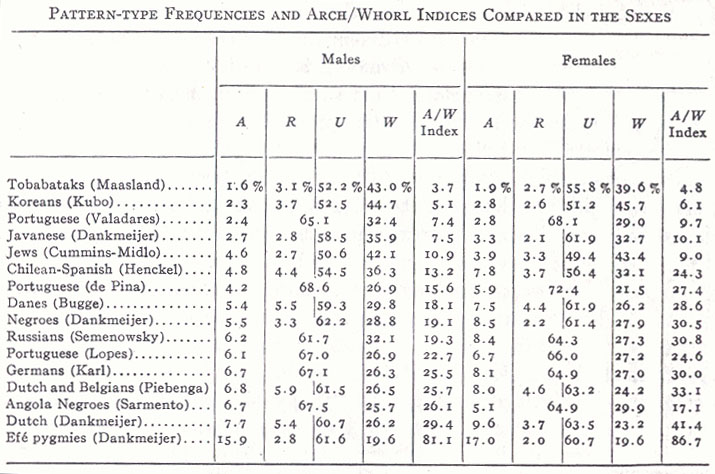
Cummins & Midlo (1943) also presented in their work an overview of studies 16 populations around the world (see the figure below):
- arches were more common in females in 87.5% of the populations (14 out 16 studies);
- whorls were more common in males in 65.6% of the populations (10.5 out of 16 studies).
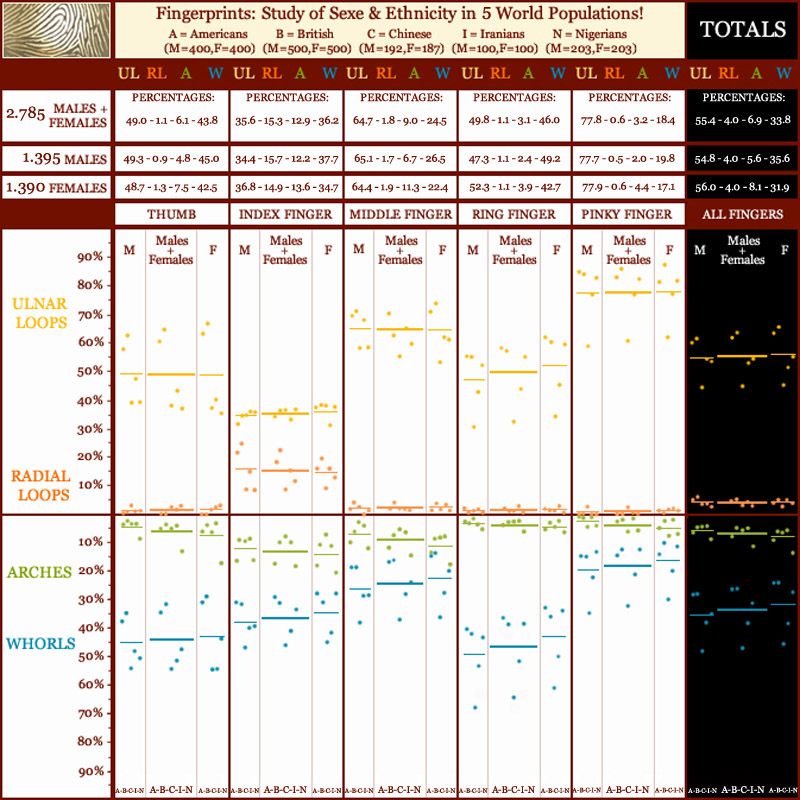
And more recent studies have revealed the same tendencies among e.g. Americans, Britains, Chinese, Iranians & Nigerians; in all 5 populations arches are more common among females, and in 4 out of 5 populations whorls are more common among males - see the picture below ('click' on the picture for a high resolution image).
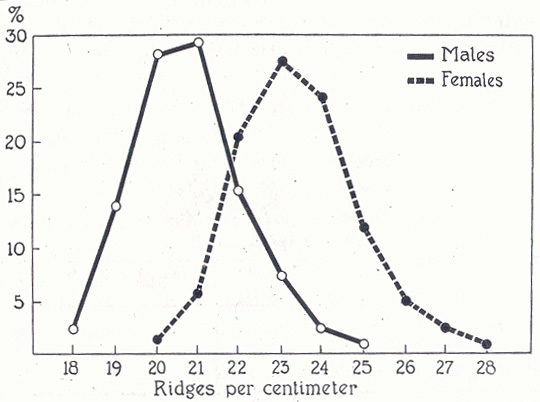
Ridge breadth is typically higher in males (compared to females). The average ridge width (considering all fingerprint zones and palmar areas) in young males is about 20.7 ridges per centimeter, in young females the average is about 23.4: see the picture below (taken from: 'Finger Prints, Palms and Soles', Cummins & Midlo
NOTICE: The sexe difference in (fingerprint) 'ridge breadth' is relatively about twice as high as the typical sexe difference seen for 'body height'!
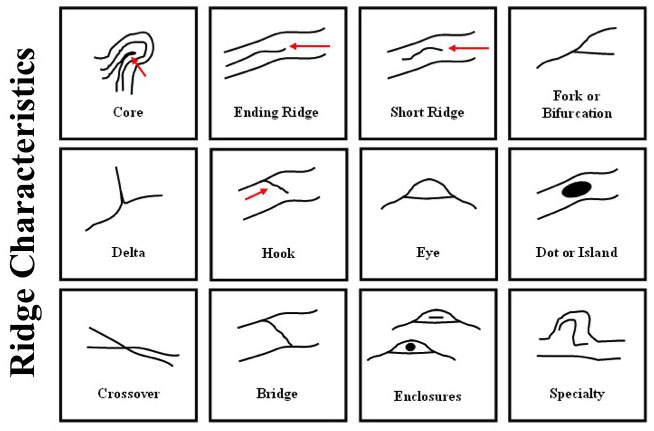
In 2010 a Thai study revealed that ridge irregulaties (e.g. ridge dots, short ridges, ridge spurs) are generally more common in the fingerprints of males (compared to females).
Bifurcations are seen in all subjects (all males & all females).
NOTE: The study of the so-called 'minutiae' involves friction ridge skin variations that can manifest as e.g.:
- Core shape: a U-turn in the ridge pattern;
- Ridge ending: the abrupt end of a ridge;
- Short ridge, or independent ridge: a ridge that commences, travels a short distance and then ends
- Ridge bifurcation (fork): a single ridge that divides into two ridges
- Delta shape: a Y-shaped ridge meeting (triradius);
- Hook (or spur): a bifurcation with a short ridge branching off a longer ridge
- Eye
- Island: a single small ridge inside a short ridge or ridge ending that is not connected to all other ridges
- Crossover or bridge: a short ridge that runs between two parallel ridges
- Bridge
- Ridge enclosure: a single ridge that bifurcates and reunites shortly afterward to continue as a single ridge
- Speciality (various).
How do fingerprints related to ethnicity/race? ...more.
![]() FINGERPRINTS INDEX:
FINGERPRINTS INDEX:
INTRO: Fingerprint Distributions & Hand Diagnostics
• HISTORY of Fingerprints
• CLASSIFICATION of Fingerprints
• SEXE DIFFERENCES & Fingerprints
• ETHNIC DIFFERENCES & Fingerprints
• DISEASES & Fingerprints
• Fingerprints & BEHAVIOR!
• FINGERPRINT DISTRIBUTIONS on the 5 Fingers
• WORLD MAP of Fingerprints
• 10 Facts about radial loop fingerprints
• 10 Facts about arch fingerprints
• MORE NEWS about Fingerprints (+ Palm Dermatoglyphics)
• Dermatoglyphics Multiple Intelligence Test {Review]




ULNAR LOOP - WHORL - RADIAL LOOP - ARCH
![]() FINGERPRINT DIAGNOSTICS:
FINGERPRINT DIAGNOSTICS:
• Fingerprints in DIABETES MELLITUS!
• Fingerprints in RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS!
• Fingerprints in SCHIZOPHRENIA!
• Fingerprints in DOWN SYNDROME!
• Fingerprints in FRAGILE-X SYNDROME!
_(In autism 2% to 6% have Fragile-X syndrome!)
Video: Mythbusters beat fingerprints system
• The hand lines (palmar creases)
• The simian line
• The Sydney line
• The Hypothenar whorl
• What can finger length reveal?
• The 5th finger (pinky)
• The fingernail tutor

EARLY HAND DIAGNOSTICS:
& HANDS ON HEALTH CARE!!
Always be aware: even though fingerprints bare the potential to show significant clues for aspects of personality, diseases & syndromes, multiple perspectives of the hand need to be taken in consideration in order to make a well substantiated reliable assessment or diagnosis.
The no.1 rule in Multi-Perspective Hand Reading describes the fundamental major principle where scientific hand reading begins: